Transparent LED screen and film screen represent two advanced yet fundamentally different approaches to modern transparent display technology. As demand surges for visually striking, space-efficient, and interactive display solutions in architecture, retail, and transportation sectors, understanding the core differences between these two technologies becomes essential. While both aim to deliver content without blocking natural light or obstructing views, their underlying structures, performance characteristics, and integration methods vary significantly.
To make informed decisions—whether for architectural display integration, retail window design, or industrial control systems—it’s crucial to look past marketing buzzwords and explore the technical foundations and performance trade-offs of each solution. Only by examining factors such as pixel structure, transparency ratio, brightness capacity, installation requirements, and long-term durability can decision-makers choose the most appropriate display technology for their specific context.
1. How to choose between transparent LED screen and film screen
Making the right choice between a transparent LED display and a film-based transparent display requires a clear understanding of application-specific priorities. It’s not just a matter of aesthetics—it’s about matching the technical strengths of each system to the operational environment and functional goals.
Here’s a decision matrix to help guide the selection:
| Application Scenario | Best Choice | Key Reason |
| Outdoor Digital Signage | Transparent LED | High brightness, weather-resistant, long-distance visibility |
| Indoor Retail Windows | Film Display | Ultra-light, high transparency, minimalist installation |
| Architectural Media Facades | Transparent LED | Large-scale scalability, pixel mapping, high refresh rates |
| Museum or Gallery Glass | Film Display | Subtle integration, low heat output, compatible with sensitive environments |
| Automotive HUD or Smart Glass | Film Display | Lightweight, curved surface adhesion, low power |
| Shopping Mall Atriums | Transparent LED | Modular maintenance, ambient light performance, interactivity integration |
Also consider:
- If dynamic brightness control, modular design, and ruggedness are priorities, LED is superior.
- If weight, form factor, and clean aesthetic dominate your requirement list, film screens are ideal.
Ultimately, the best technology is the one that aligns with how and where you plan to communicate your content.

2. Transparent LED vs Film Screen Cost Comparison
When evaluating transparent LED displays and film-based transparent screens, cost considerations go far beyond just the initial purchase price. It’s crucial to factor in total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes installation complexity, structural support requirements, maintenance, and long-term energy consumption.
Below is a comparative breakdown of the typical cost components for each technology:
| Cost Component | Transparent LED Display | Transparent Film Screen |
| Initial Hardware Cost | High – due to pixel modules, controller cards | Moderate – film materials are cheaper per m² |
| Installation | High – requires structural frame or steel support | Low – self-adhesive, often retrofitted to existing glass |
| Weight Load Costs | Significant – may need reinforcement | Minimal – ultra-lightweight film material |
| Power Consumption | Higher – needs active cooling in some cases | Lower – passive or semi-active light emission |
| Maintenance | Moderate – modules can be serviced individually | Low – few moving parts, but replacement can be costly |
| Lifespan (avg.) | 50,000–100,000 hours | 20,000–30,000 hours |
| Long-Term ROI | High for large-format advertising or branding | High for retail and interior enhancement |
From a capital expenditure perspective, transparent LED screens generally require a higher upfront investment—particularly for large displays where structural support and high brightness are critical. However, their longer lifespan and modular maintenance may justify the cost in commercial applications like airports, outdoor malls, or media facades.
Film screens, while cheaper to install and almost invisible when powered off, may face limitations in scalability and performance degradation over time. They’re ideal for use cases where aesthetic integration and minimal disruption are prioritized over high refresh rates or 24/7 operation.
In summary, if your project demands durability, brightness, and performance, transparent LED screens deliver a stronger long-term value. But for budget-sensitive, design-focused applications, film screens offer compelling advantages in form factor and ease of deployment.

3. Core Display Architecture
At a hardware level, the construction methods of transparent LED screens and film screens diverge drastically:
| Component | Transparent LED Screen | Transparent Film Screen |
| Display Driver | Discrete driver ICs per LED cluster | Embedded TFT/ITO driver matrix |
| Pixel Source | Surface-mounted LED chips (SMD or COB) | Transparent micro-LED or OLED integrated into film |
| Substrate | Polycarbonate or aluminum PCB frame | PET or polyimide-based transparent film |
| Connectivity | Copper busbars with power/data daisy-chain | Transparent conductive ITO/graphene grid |
| Control Interface | External sending/receiving cards (NovaStar, Colorlight) | Integrated media control via HDMI or USB (for simpler setups) |
In transparent LED screens, pixels are physically spaced on a grid of LED strips, which are either SMD-based or COB-based, depending on pitch and design requirements. Film screens, in contrast, employ ultra-thin transparent substrates embedded with nanometer-scale pixels, often using micro-LED or transparent OLED technologies.
4. Display Physics: Brightness, Pitch, and Transparency
Light Transmission vs. Emission is where the real magic—and difference—happens.
Transparent LED Screens
Transparent LED screens are active light-emitting displays. Each pixel emits its own light, achieving brightness levels of 4000 to 7000 nits, sufficient for direct sunlight. Because LEDs are spaced apart, the light can pass between them, achieving a transparency rate of 60%–90% depending on pixel pitch (P2.8 to P10+). The larger the pitch, the more transparent—but the lower the resolution.
Transparent Film Screens
These rely on light modulation instead of emission. Film screens usually have lower pixel density and rely on ambient or backlight illumination, leading to lower brightness (typically <1000 nits). Though they often boast higher transparency (~85–95%), they lack the power to compete in direct light environments. Also, because pixels are fixed in the film, scalability is constrained.
5. Pixel Management & Refresh Control
A major technical divergence lies in signal processing and pixel control.
- LED Screens use dedicated receiver cards (such as NovaStar A8s) that allow for dynamic refresh rate control (up to 3840Hz), grayscale management, and color calibration. Each module is addressable and can adapt in large video walls or curved installations.
- Film Screens, especially those based on transparent OLED, typically have integrated matrix addressing. While some high-end solutions offer refresh rates around 120Hz, the lack of modular control means they can’t scale without significant performance drop.
This becomes crucial in use cases involving high frame-rate video, camera synchronization, or augmented reality overlays.
6. Heat Dissipation and Power Distribution
Transparent LED Screens:
- Consume 60–120 W/m², depending on pitch and brightness.
- Have embedded aluminum PCB or metal frame to assist passive cooling.
- Larger systems often include active cooling modules or heat pipes.
Film Screens:
- Consume far less, usually 10–30 W/m².
- Use thin-layer graphene or ITO circuits for passive dissipation.
- But are more thermally sensitive, especially OLED-based models that degrade under continuous high brightness.

7. Mechanical and Electrical Integration
Transparent LED screens require a metal structural frame to mount LED strips and carry power and data buses. Their weight ranges from 10–20kg/m². They are engineered for modular replacement, making maintenance easier in large installations.
Film screens are thin (under 2mm) and light (<1kg/m²). They can be laminated directly onto existing glass using optical adhesives. However, once applied, removing or replacing the film often causes damage. Also, they demand flat, dust-free application environments to avoid pixel contamination.
8. Visual Performance Metrics
| Performance Metric | Transparent LED Screen | Transparent Film Screen |
| Contrast Ratio | 5000:1 to 10000:1 | 1500:1 to 3000:1 |
| Viewing Angle | Up to 160° | Up to 120°, limited on horizontal axis |
| Color Gamut | Rec. 709 / Rec. 2020 (with calibration) | Limited by pixel tech (sRGB for OLED) |
| Grayscale Depth | 14–16 bit | 8–10 bit |
While film screens can look sleek, transparent LED screens win when raw performance is needed.
Q&A – In-Depth Technical Questions
Q1: Can film screens be used in outdoor sunlight environments?
Not reliably. Their luminance isn’t strong enough to overpower ambient light, making them almost invisible under direct sun.
Q2: How scalable are transparent LED systems for building façades?
Highly scalable. You can build displays of hundreds of square meters due to modular panel design, long-distance signal cascading, and redundancy options.
Q3: Are there transparent LED solutions with flexible substrates like film?
Yes. Emerging flex-LED tech uses silicon or PET substrates, but they trade off pixel density and lifespan. Still, they’re gaining ground in wearable displays and auto glass.
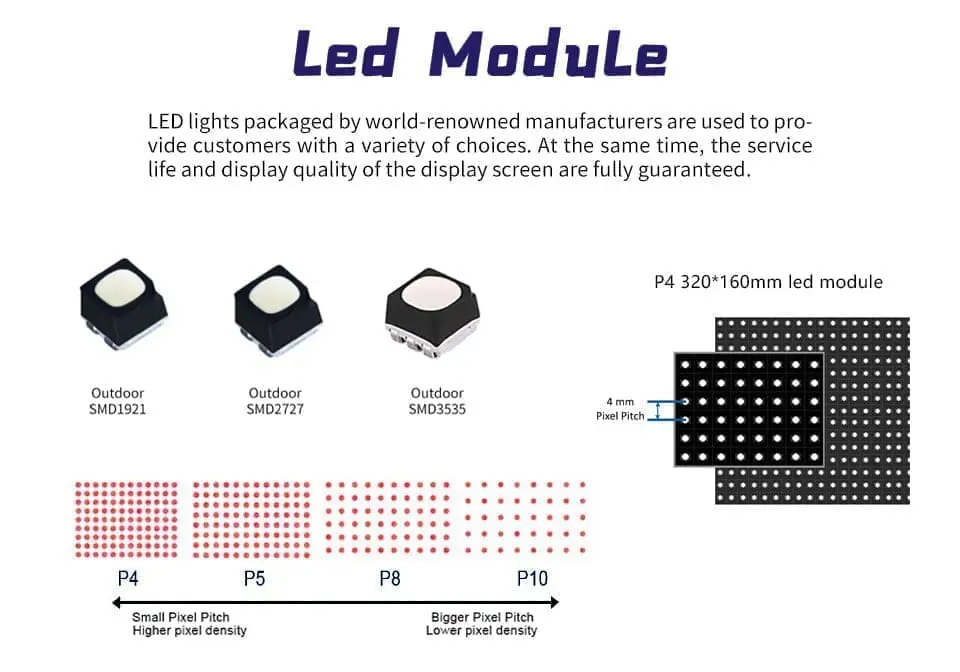
Pixel Pitch for LED Screens Display
Q4: How does pixel pitch affect transparency in LED screens?
Directly. A wider pitch means fewer LEDs per area = higher transparency, but at the cost of resolution and image sharpness.
Q5: What’s the lifespan difference between the two?
LEDs typically last 50,000–100,000 hours. OLED or micro-LED film screens degrade faster, especially blue pixels, with usable life often capped around 20,000–30,000 hours.
Q6: Are both options compatible with interactive or touch overlays?
es, but implementation differs. LED screens require IR or capacitive overlays. Film screens can integrate touch functionality during lamination using capacitive layers.
Q7: Which is more vulnerable to environmental factors like humidity?
Film screens, especially OLED-based, are more sensitive to moisture, UV, and oxygen, requiring encapsulation. LED screens are better protected and rated IP43–IP65 depending on design.
The difference between transparent LED screens and transparent film screens is not merely aesthetic—it’s structural, electrical, and functional. Choosing between them involves a trade-off between performance, integration ease, and environment.
- Use transparent LED screens where brightness, durability, and large-scale visibility are critical.
- Opt for transparent film screens where elegance, minimalism, and indoor integration take priority.
In mission-critical settings or commercial branding applications, understanding these core differences will determine whether your visual experience impresses—or disappears into the background.




















