בעולם טכנולוגיית התצוגה המתפתח ללא הרף, MicroLED ו-OLED הם שני מונחים המופיעים לעתים קרובות כשדנים בטכנולוגיות טלוויזיה ומסכים מתקדמות. לשניהם יתרונות ייחודיים, אך השאלה נותרת בעינה: האם MicroLED עדיף על OLED? כדי לענות על כך, עלינו להבין כל טכנולוגיה, כיצד היא פועלת וכיצד היא נבדלת בביצועים, בעמידות ובחסכוניות. מאמר זה יספק השוואה מפורטת בין MicroLED ל-OLED, ותעזור לכם לקבל החלטה מושכלת.
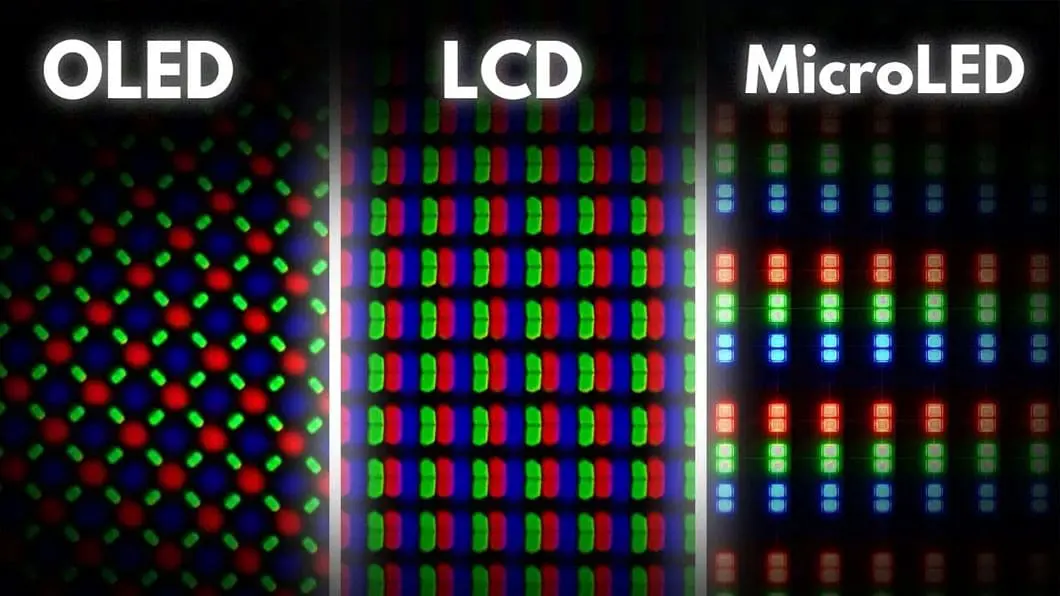
הבנת טכנולוגיית OLED
OLED (דיודה פולטת אור אורגנית) היא טכנולוגיית תצוגה שבה כל פיקסל עשוי מתרכובות אורגניות הפולטות אור כאשר זרם חשמלי עובר דרכן. בניגוד למסכי LCD מסורתיים, המסתמכים על תאורה אחורית, פאנלי OLED הם מאירים את עצמם. משמעות הדבר היא שכל פיקסל יכול להידלק ולכבות בנפרד, ומציע רמות שחור אמיתיות, ניגודיות גבוהה וצבעים עזים.
יתרונות של OLED:
- שחורים אמיתייםמסכי OLED יכולים לייצר שחורים מושלמים מכיוון שניתן לכבות לחלוטין פיקסלים בודדים.
- יחס ניגודיות מעולהעם שחורים אמיתיים, יחס הניגודיות גבוה במיוחד, וזה מושלם לצפייה בסרטים או משחקי וידאו בסביבות חשוכות.
- עיצוב דק יותרפאנלי OLED דקים וגמישים במיוחד, מה שהופך אותם לאידיאליים לעיצובים מודרניים ואלגנטיים של טלוויזיות ומסכים מעוקלים.
- זוויות צפייה רחבותצגי OLED שומרים על דיוק צבעים ובהירות כמעט מכל זווית צפייה, בניגוד לצגי LED מסורתיים, אשר עלולים לאבד ניגודיות כאשר צופים בהם מהצד.
חסרונות של OLED:
- שריפהחיסרון משמעותי אחד של טכנולוגיית OLED הוא הסיכון לצריבה (burn-in), שבה תמונות סטטיות, כמו לוגואים או רכיבי ממשק, עלולות להיצמד לצמיתות למסך אם הן מוצגות זמן רב מדי.
- תוחלת חייםלמרות שמסכי OLED הם בדרך כלל עמידים לאורך זמן, החומרים האורגניים שלהם מתכלים עם הזמן, מה שיכול להשפיע על דיוק הצבעים והבהירות.
- מְחִירמסכי OLED עדיין יקרים לייצור, מה שהופך אותם ליקרים יותר בהשוואה לטכנולוגיות תצוגה אחרות, כגון LED ו-LCD.
הבנת טכנולוגיית MicroLED
מיקרולד היא טכנולוגיית תצוגה חדשה יותר המשתמשת בנורות LED מיקרוסקופיות כדי ליצור כל פיקסל. בניגוד ל-OLED, שמסתמך על תרכובות אורגניות, MicroLED משתמש בנורות LED אנאורגניות כדי לפלוט אור. צגי MicroLED הם מודולריים, כלומר ניתן ליצור אותם על ידי הרכבת פאנלים בודדים ליצירת צגים גדולים יותר, מה שהופך אותם לניתנים להתאמה אישית רבה.
יתרונות של מיקרולד:
- רמות שחור מושלמותכמו OLED, MicroLED יכול להשיג שחורים אמיתיים על ידי כיבוי נוריות LED בודדות. מכיוון שכל פיקסל הוא מקור אור עצמאי, אין זרימה של תאורה אחורית, וכתוצאה מכך ניגודיות מושלמת.
- אין צריבהאחד היתרונות המשמעותיים ביותר של MicroLED על פני OLED הוא שהוא חסין מפני צריבה. מכיוון ש-MicroLED משתמש בחומרים אנאורגניים, הסיכון לשמירת תמונה או צריבה קבועה מבוטל.
- תוחלת חיים ארוכה יותרלצגי MicroLED אורך חיים ארוך יותר מאשר לצגי OLED מכיוון שהחומרים האנורגניים בהם נעשה שימוש עמידים יותר ופחות נוטים להתקלקל עם הזמן.
- בהירות ועמידותפאנלי MicroLED יכולים להשיג רמות בהירות גבוהות יותר בהשוואה ל-OLED, מה שהופך אותם למתאימים יותר לסביבות בהירות. בנוסף, הם יכולים לשמור על בהירות עקבית ללא סיכון של שחיקה.
- מדרגיותצגי MicroLED ניתנים להרחבה בקלות. האופי המודולרי של MicroLED מאפשר ליצרנים לבנות צגים בכל גודל ויחס גובה-רוחב, החל ממסכים קטנים ועד קירות וידאו ענקיים.
חסרונות של מיקרולד:
- עֲלוּתנכון לעכשיו, טכנולוגיית MicroLED יקרה יחסית, בעיקר בגלל תהליך הייצור המורכב. עלות הייצור צפויה לרדת ככל שהטכנולוגיה תתבגר.
- עוֹבִיבעוד שצגי MicroLED יכולים להיות דקים יחסית, הם אינם דקים כמו צגי OLED. פאנלי MicroLED דורשים יותר מקום עבור מודולי ה-LED וייתכן שלא יהיו אלגנטיים באותה מידה.
- זמינות מוגבלתטכנולוגיית MicroLED עדיין בשלביה הראשונים, עם מוצרים מוגבלים הזמינים בשוק בהשוואה ל-OLED, שקיימת כבר זמן רב יותר.
השוואה בין MicroLED ל-OLED: מה עדיף?
1. איכות תמונה: שְׁנֵיהֶם מיקרולד ו OLED מצטיינים באספקת איכות תמונה מעולה. שניהם מציעים שחורים אמיתיים, יחסי ניגודיות גבוהים וצבעים עזים. עם זאת, מיקרולד לוקחים את היתרון בכל הנוגע לבהירות. צגי MicroLED יכולים לייצר רמות גבוהות יותר של בהירות מבלי לפגוע באיכות התמונה, מה שהופך אותם לבחירה טובה יותר עבור חדרים מוארים או צגים חיצוניים. OLED, לעומת זאת, זורח בסביבות חשוכות, שם בולטים באמת הצבעים השחורים העמוקים והניגודיות הגבוהה שלו.
2. עמידות ואורך חיים: מבחינת אורך חיים, מיקרולד יש יתרון ברור על פני OLEDמסכי OLED נוטים להתבלות עם הזמן, במיוחד מבחינת דיוק הצבעים והבהירות, ככל שהחומרים האורגניים שלהם נשחקים. ל-MicroLED, עם נוריות ה-LED האנאורגניות שלה, אורך חיים ארוך בהרבה והיא עמידה בפני שחיקה, מה שהופך אותה לבחירה טובה יותר לשימוש ארוך טווח.
3. סיכון של כוויה: שריפה היא אחד החסרונות המשמעותיים ביותר של OLED טכנולוגיה. אם תמונות סטטיות מוצגות למשך זמן רב מדי, הן עלולות להשאיר סימנים קבועים על המסך. זה בעייתי במיוחד עבור משתמשים המתכננים להשתמש בצג שלהם לפעילויות הכוללות אלמנטים סטטיים, כמו משחקי וידאו או ערוצי חדשות עם לוגואים קבועים. מיקרולדעם זאת, חסין מפני צריבה, מה שהופך אותו לבחירה בטוחה יותר לשימוש ארוך טווח מבלי לדאוג לשמירת תמונה.
4. עלות: כַּיוֹם, OLED תצוגות הן זולות ונגישות יותר מאשר מיקרולד, אשר עדיין נמצאת בחיתוליה. מיקרולד ייצור הטכנולוגיה יקר יותר עקב מורכבות ייצור נורות מיקרו-לד בודדות. עם זאת, ככל שהטכנולוגיה הופכת נפוצה יותר ושיטות הייצור משתפרות, עלות מיקרולד צפוי לרדת.
5. גמישות ועיצוב: OLED הצגים דקים במיוחד וגמישים, מה שהופך אותם לאידיאליים לעיצובי מסכים מעוקלים וגמישים. הגמישות מאפשרת ליצרנים ליצור עיצובים ייחודיים ומסוגננים, כולל צגים מתקפלים או מתגלגלים. מיקרולד, למרות שדק יותר ממסכי LED מסורתיים, אינו גמיש כמו OLED. עם זאת, האופי המודולרי של MicroLED מאפשר מסכים הניתנים להרחבה הניתנים להתאמה אישית לגדלים ויחסי גובה-רוחב שונים, מה שהופך אותו מתאים ליישומים בקנה מידה גדול.
איזה מהם מתאים לך?
אז, האם מיקרולד טוב יותר מ OLEDזה תלוי מה אתה מחפש בתצוגה. אם אתה נותן עדיפות איכות התמונה, מיקרולד מציע בהירות וניגודיות מעולים, יחד עם העמידות של חומרים אנאורגניים. אם אתם מחפשים תוחלת חיים ארוכה יותר ורוצים להימנע מבעיות של צריבה, מיקרולד היא האפשרות הטובה יותר. עם זאת, OLED עדיין זורח מבחינת סבירות ו גְמִישׁוּת, והוא נותר הבחירה המועדפת עבור צרכנים המחפשים תצוגה איכותית, אלגנטית ובמחיר סביר.
למי שמחפש ביצועים פרימיום ו טכנולוגיה מתקדמת, מיקרולד הוא ללא ספק עתיד טכנולוגיית התצוגה, אבל לעת עתה, OLED נותרה האפשרות הנגישה יותר עם ביצועים מצוינים במחיר נמוך יותר. הבחירה הסופית תלויה בצרכים האישיים, בתקציב ובהעדפות שלכם.
ככל שטכנולוגיות התצוגה ממשיכות להתפתח, גם מיקרולד ו OLED צפויים למלא תפקידים מרכזיים בעיצוב עתיד הבידור הביתי, המשחקים ויישומי תצוגה מקצועיים.













